Product identification is the foundation of accurate product matching in Google Shopping. Among all product identifiers, MPN (Manufacturer Part Number) plays a critical role when GTINs are missing or unavailable. Many Google Shopping issues—poor visibility, mismatched listings, disapproved products, or weak ad performance—can be traced back to incorrect or missing MPN data. This guide explains what Google Shopping MPN is, how it works, when it is required, and how to implement it correctly for maximum performance.
What Is MPN in Google Shopping?
MPN (Manufacturer Part Number) is a unique identifier assigned by the manufacturer to represent a specific product model.
Unlike internal seller identifiers:
-
SKU → created by the seller
-
MPN → created by the manufacturer
-
GTIN → global barcode standard
Google uses MPN to understand exact product identity, especially when no GTIN exists.
MPN helps Google determine:
-
Whether two products from different sellers are the same
-
How products should be grouped in Shopping results
-
Which listings should compete on price and availability
Why MPN Is Important in Google Shopping
Google Shopping is built on product accuracy and comparability.
MPN helps Google:
-
Identify identical products across merchants
-
Prevent duplicate or incorrect product listings
-
Improve price comparison accuracy
-
Increase relevance of Shopping Ads
-
Strengthen trust in merchant data
Without a valid MPN, Google may rely on weaker signals such as title text or images, which can lead to mismatches and reduced visibility.
How Google Uses MPN Internally


Google does not rely on MPN alone.
It combines MPN with other attributes to form a product identity profile, including:
-
Brand
-
Product title
-
Product images
-
Category classification
-
Structured attributes (color, size, material)
When Brand + MPN are accurate and consistent, Google can confidently group products and rank them correctly.
When Is MPN Required in Google Shopping?
You must submit MPN if all of the following conditions are met:
-
The product is new
-
The product is not custom-made
-
The product does not have a GTIN
-
The manufacturer provides an MPN
If any of these conditions are not met, MPN may not be required.
When MPN Is Not Required
You should not submit MPN when the product falls into one of the following categories:
-
Custom-made or handmade products
-
Private-label products with no manufacturer identifier
-
Used or vintage products
-
Products sold without an assigned manufacturer part number
In these cases, you must explicitly tell Google that identifiers do not exist by setting:
identifier_exists = no
Failing to do this can lead to feed warnings or disapprovals.
MPN vs GTIN vs Brand (Critical Difference)
| Attribute | Purpose | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| GTIN | Global barcode identifier | Highest |
| MPN | Manufacturer model identifier | High |
| Brand | Manufacturer name | Mandatory with MPN |
Important rule:
If you submit MPN, you must also submit Brand.
Google uses Brand + MPN together as a unique product key.
Example of a Correct MPN Implementation
Product title: Samsung Galaxy S21 128GB Phantom Gray
Brand: Samsung
MPN: SM-G991B
GTIN: Not available
This setup allows Google to:
-
Match your listing with identical Samsung Galaxy S21 products
-
Group listings correctly in Shopping results
-
Display accurate price comparisons
Common MPN Mistakes (Major Cause of Poor Performance)
Avoid these common errors:
1. Using SKU as MPN
SKUs are seller-defined and not valid manufacturer identifiers.
2. Using Generic Values
Never use values such as:
-
“N/A”
-
“Unknown”
-
“123456”
-
“Default”
3. Reusing the Same MPN
Each product model must have a unique MPN.
4. Incorrect Brand–MPN Pairing
Wrong combinations confuse Google and reduce product matching accuracy.
MPN for Private Label Products
Private label products often cause confusion.
If You Manufacture the Product
You may:
-
Create a unique internal MPN
-
Use your registered brand name
-
Keep the MPN consistent across all platforms
If No Manufacturer Identifier Exists
Do not invent one.
Instead, use:
identifier_exists = no
Consistency is more important than creativity.
How to Add MPNs in Google Shopping Feed and Merchant Center (Step-by-Step)
Adding MPNs (Manufacturer Part Numbers) to your Google Shopping feed is a structured process. While it’s not technically complex, accuracy is critical—small mistakes can lead to feed warnings, mismatched products, or limited performance in Google Merchant Center.
Below is a step-by-step process to correctly add MPNs to your Google Shopping feed and ensure they are properly recognized by Google Merchant Center.
Step 1: Gather MPN Information for Each Product
Start by collecting the correct MPNs for all eligible products.
MPNs must come directly from the manufacturer. Before updating your feed, verify that:
-
The product actually has a manufacturer-assigned MPN
-
The MPN is accurate and complete
-
Variants (size, color, model) have their own distinct MPNs, if applicable
It’s recommended to compile all MPNs in a Google Sheet or master file. This makes it easier to review, validate, and update data in bulk before pushing changes to your live feed.
Step 2: Prepare Your Feed File or System for MPN
Once you have the correct MPNs, the next step is to prepare your feed to accept them. The method depends on the feed format you’re using.
Using a Spreadsheet or CSV Feed
-
Add a new column with the header:
mpn (all lowercase) -
Each row under this column should contain the MPN for the corresponding product or variant
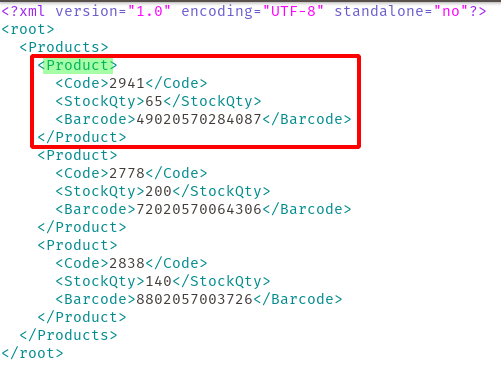
If You Are Using an XML Feed
-
Add the MPN attribute within each product node using the following format:
<g:mpn>ISP-78UE</g:mpn>
If You Are Using Content API or Feed Management Tools
-
Locate the MPN field within your feed tool
-
Map your internal MPN data source to the Google Shopping
mpnattribute -
Ensure the field is enabled and not excluded during sync
Step 3: Insert MPN Values Correctly

Populate the MPN field with the exact value provided by the manufacturer.
For example:
-
If the manufacturer’s MPN is ISP-78UE, enter ISP-78UE
-
Maintain the original formatting, including:
-
Hyphens
-
Capitalization
-
Spaces (if any)
-
Do not:
-
Modify the format
-
Convert to lowercase if it was originally uppercase
-
Add extra spaces before or after the value
Even small typos or formatting inconsistencies can cause data mismatches and negatively affect feed quality.
Step 4: Add Other Relevant Product Identifiers

MPN works best when combined with other identifiers.
Whenever available, include:
-
GTIN (UPC, EAN, ISBN)
-
Brand
-
MPN
Providing multiple identifiers helps Google:
-
Match products more accurately
-
Group identical listings correctly
-
Improve eligibility across Shopping placements
If a product does not have a GTIN but does have an MPN, Brand + MPN becomes essential.
Step 5: Upload the Updated Feed to Google Merchant Center

Once your feed is updated with MPN values, upload it to Google Merchant Center using your preferred method:
-
Manual upload
-
Scheduled fetch
-
Automated sync via feed tools or platforms
Ensure the upload completes successfully and that no file processing errors occur.
Step 6: Verify and Troubleshoot MPN Issues
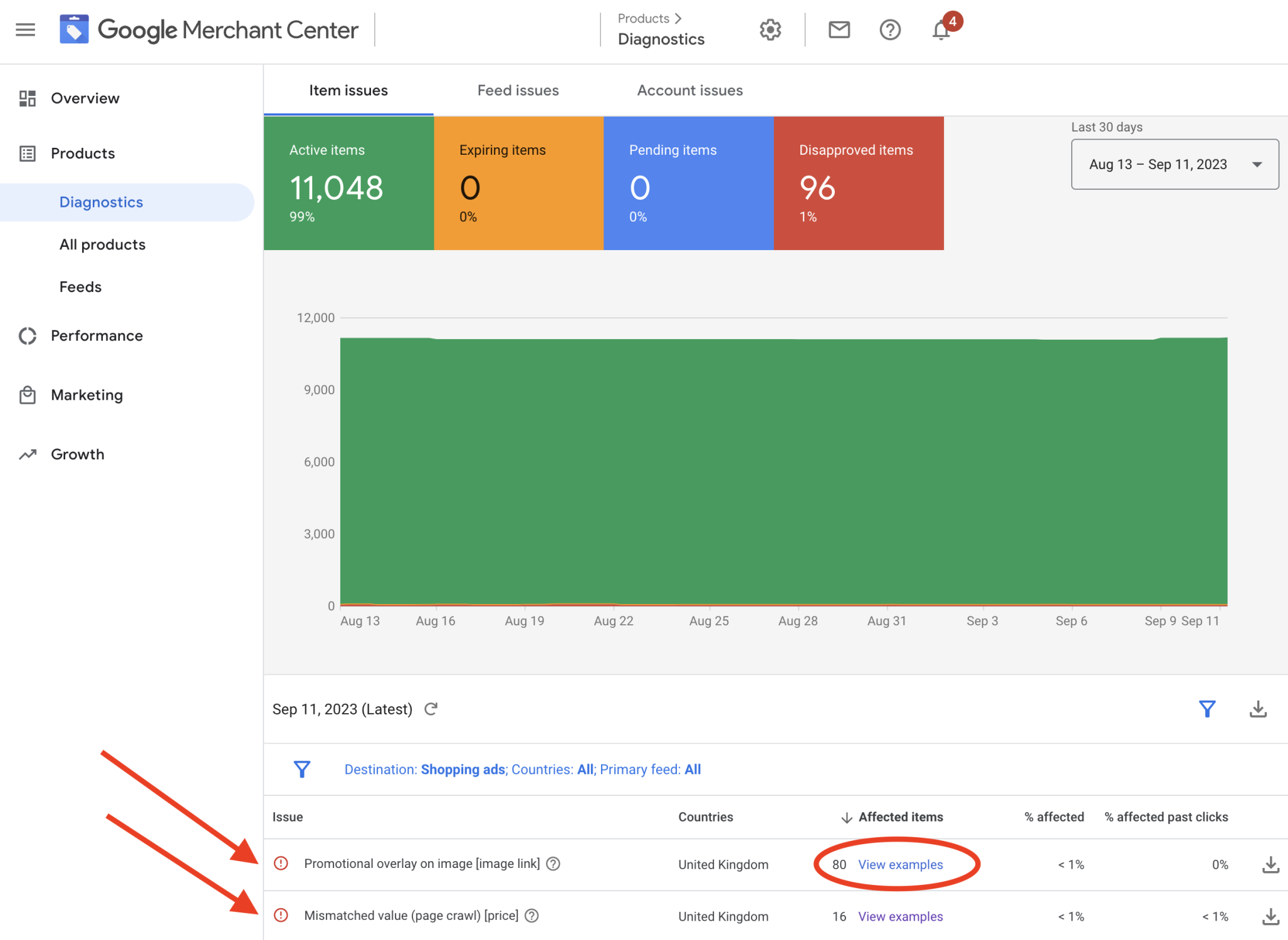

After uploading, monitor your account closely.
Go to:
Merchant Center → Products → Diagnostics → Needs Attention
Check for:
-
Missing MPN warnings
-
Incorrect identifier errors
-
“Limited performance due to missing identifiers” messages
If issues appear:
-
Recheck formatting
-
Confirm the MPN matches manufacturer data
-
Ensure the value is applied at the correct product or variant level
If no issues appear after several days, your feed has been successfully processed with valid MPN values.
Important Tips
-
Always use manufacturer-provided MPNs
-
Never guess or auto-generate MPN values
-
Store MPNs at the variant level when applicable
-
Combine MPN with Brand and GTIN whenever possible
-
Treat identifier warnings as performance issues, not minor alerts
Correct MPN implementation improves feed accuracy, product matching, and long-term Shopping performance.
MPN and Visual Search (Google Lens)

MPN supports Google’s visual shopping ecosystem by helping Google connect visual matches with exact product listings.
When a user searches using an image:
-
Visual similarity identifies candidates
-
MPN confirms product identity
-
Accurate listings appear in results
This makes MPN increasingly important for future-facing search behavior.
SEO Benefits of Correct MPN Data
While MPN is not a traditional SEO ranking factor, it indirectly improves:
-
Product discoverability
-
Shopping Graph accuracy
-
Trust signals across Google surfaces
-
Free product listing visibility
Strong identifiers lead to stronger ecosystem placement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is MPN mandatory in Google Shopping?
Only when the product is new, branded, and has no GTIN.
Can SKU be used as MPN?
No. SKU is not a manufacturer identifier.
What happens if MPN is missing?
Google may struggle to match your product, leading to lower visibility.
Is MPN required for handmade products?
No. Use identifier_exists = no.
Can incorrect MPN cause disapproval?
Yes. Incorrect identifiers are a common cause of feed issues.
Best Practices Summary
-
Always use the manufacturer’s official MPN
-
Never confuse SKU with MPN
-
Always submit Brand with MPN
-
Keep MPN consistent across feeds
-
Use
identifier_exists = nowhen applicable
Final Summary
MPN in Google Shopping is a manufacturer-assigned product identifier used to accurately match, group, and rank products when GTINs are unavailable. Correct MPN implementation improves visibility, reduces feed errors, strengthens Shopping Ads performance, and supports visual search experiences across Google platforms.



