What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
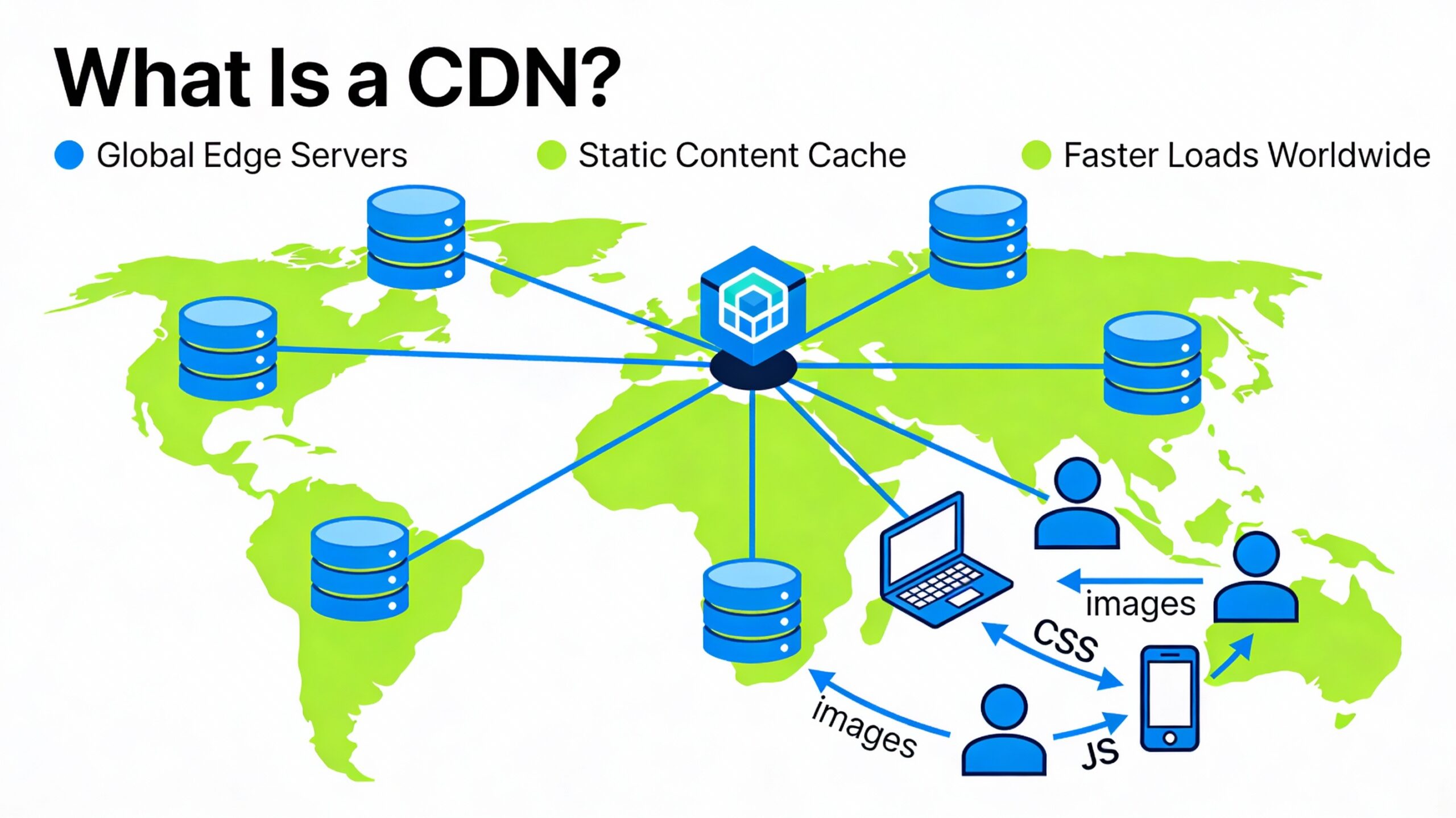
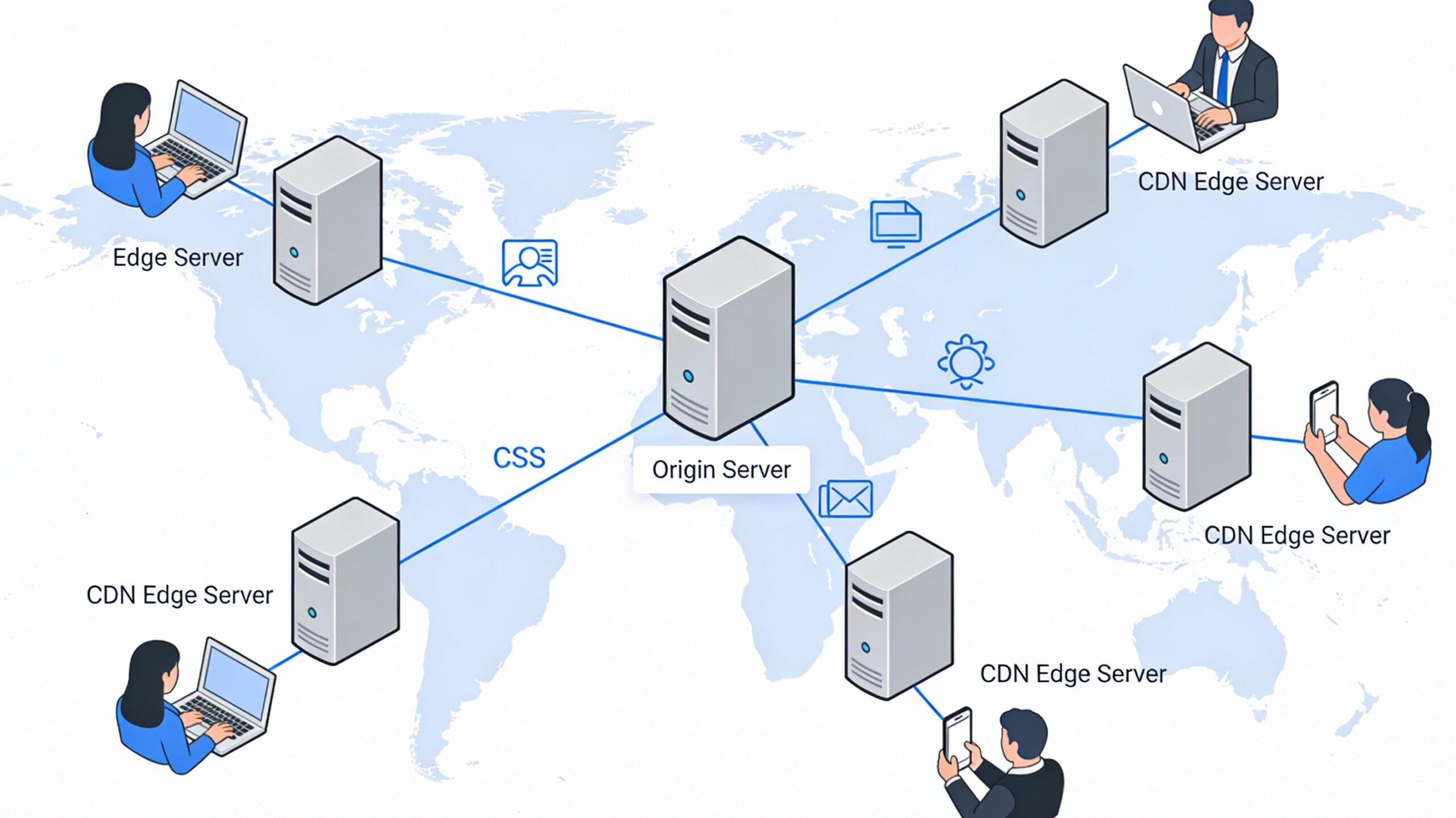
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of servers distributed across different locations around the world. It helps deliver static website content—such as images, CSS, JavaScript, and videos—from the server closest to the user. These servers are known as edge servers.
Instead of every visitor accessing your website from a single main hosting server, a CDN stores copies of your content on multiple edge servers globally. This reduces the distance data needs to travel, resulting in faster page load times, lower server load, and reduced bandwidth usage. By improving website speed and performance, a CDN enhances user experience and supports better SEO results.
How Does CDN Work?
A CDN stores copies of your website on several edge servers across the world. When a user accesses your website, the CDN immediately delivers content from the server closest to them. It speeds up website loading by reducing data travel distances and relieving pressure on your primary server, reducing the danger of a crash.
What kind of Content CDN Deliver?
A CDN mostly distributes static content—portions of your website that do not change between visits but are large in size and sluggish to load. These files are duplicated and stored on CDN servers around the world, allowing for instant loading. CDNs typically deliver:
- Images (jpg, png, webp, logos, and banners
- Videos (mp4, promotional videos, product demonstrations
- CSS files (styles that affect how the page appears
- JavaScript files (scripts that enable site features
- HTML pages
- Fonts
- PDFs and Downloads
What CDNs typically don’t deliver
- Dynamic material that changes for each user (similar to personalised dashboards).
- Real-time data (real stock prices and conversation messages)
Why Do Websites Need Content Delivery Network Services?
Websites use CDN services to ensure web pages load quickly and smoothly, improving the user experience for users worldwide. Without a CDN, all visitors connect to a single central server, causing slowdowns or overloads for users globally.
A CDN stores copies of static content (images, videos, and scripts) on servers around the world and serves them to visitors based on their geographic location. This results in increased stability, faster loading regardless of location, reduced burden on the origin server, less downtime during peak traffic, easier handling of large files, fewer crashes, improved Google Core Web Vitals, and better SEO.
Key SEO Advantages of Using A CDN
Using a CDN aligns with modern SEO best practices, primarily by improving site speed and user experience. Here’s a comprehensive list of significant SEO benefits:
Improved Page Load Speed – Page speed has a direct impact on Google rankings, particularly mobile, with faster timings decreasing bounce rates and increasing Core Web Vitals.
Reduced Latency– CDNs cache static files on global edge servers, allowing users to download from the closest one, reducing wait times.
Enhanced Core Web Vitals – Enhances Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) with nearby large file delivery, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) with quick JS/CSS, and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) by stabilising elements.
Increased uptime and reliability (DDoS protection) – Distributes traffic across servers to handle surges or attacks, keeping websites operational for improved crawling and ranking.
Improved Local Performance – Serves files from local edge servers, which benefits international SEO.
Improved Crawl Efficiency – Reduces origin server load, resulting in faster Googlebot responses and more indexing.
Security Benefits – Provides SSL, bot protection, and virus prevention at the edges.
Boost mobile SEO – Ensures quick mobile experiences with mobile-first indexing.
Why Do Modern Websites Need a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
CDNs are vital today because of the speed-distance matrix: sites that take more than 3 seconds to load abandon 53% of the time. Traffic spikes from viral posts or sales overwhelm individual servers, but CDNs distribute the burden.
Security risks such as DDoS and bot attacks are on the rise; CDNs provide WAF protection at the edge. They save money by reducing revenue loss from downtime, ensuring consistent performance across devices, and handling spikes to improve conversions.
Which Websites Benefit the Most from CDNs?
- E-commerce Stores – Reduces load times for worldwide shopping, increases conversions, manages sales traffic, enhances SEO, and secures transactions.
- News & Media Websites – Handles media-heavy spikes from viral events, lowering bounce rates and increasing engagement.
- SaaS Platforms – Delivers static assets reliably around the world for a consistent user experience.
- Websites with Global Traffic – Uses local edges to improve slow loading for international consumers.
- Content-heavy Websites – Optimises huge assets for sites such as WordPress blogs or video streaming services.
- SEO Websites- Maintains top ranks through speed, stability, and Core Web Vitals.
- Websites with Paid Ads – Increases ad ROI through rapid page delivery.
When you don’t need a CDN?
- Small, local, and light websites – Sites have primarily local users, as hosting is already close.
- Sites with low traffic, few fast-loading pages, and minimal heavy assets.
CDN vs. Web Hosting: What is the Difference?
Web hosting keeps all site files on a single or a limited number of servers, from which users can request them directly. CDN caches static content at global edges for proximity-based delivery, supplementing hosting.
| Aspect | Web Hosting | CDN |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Stores and serves all files | Caches and distributes static content |
| Location | Single or limited data centers | Global edge servers |
| Speed | Slower for distant users | Faster via proximity |
| Scalability | Via server upgrades | Auto-scales for spikes |
| Security | Basic (firewalls, SSL) | Advanced (DDoS, WAF) |
| Best For | Dynamic content, small/local sites | High-traffic, media-rich, global sites |
| Replaces the Other? | No | No—works on top of hosting |
How CDNs Help Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
CDNs improve SEO by targeting Google ranking variables such as speed. They enhance page load times by 30-70%, with 1-3 second loads rating higher.
Lower bounce rates from quick pages indicate quality to Google. Better mobile performance benefits approximately 60% of mobile searches. Consistent uptime prevents penalties, worldwide reach improves local SEO, faster crawling indexes more pages, and security measures such as DDoS protection, WAFs, and SSL ensure compliance.
| SEO Factor | How CDN Helps | Ranking Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Page Speed | Serves from nearest edge | Direct boost |
| Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS) | Reduces latency, optimizes delivery | Higher Search Console scores |
| Bounce Rate | Keeps users engaged | Indirect improvement |
| Mobile Experience | Faster delivery | Better mobile rankings |
| Uptime | DDoS protection, failover | Avoids drops |
| Crawl Budget | Quicker server responses | More pages indexed |